WHAT IS SPOOFING?
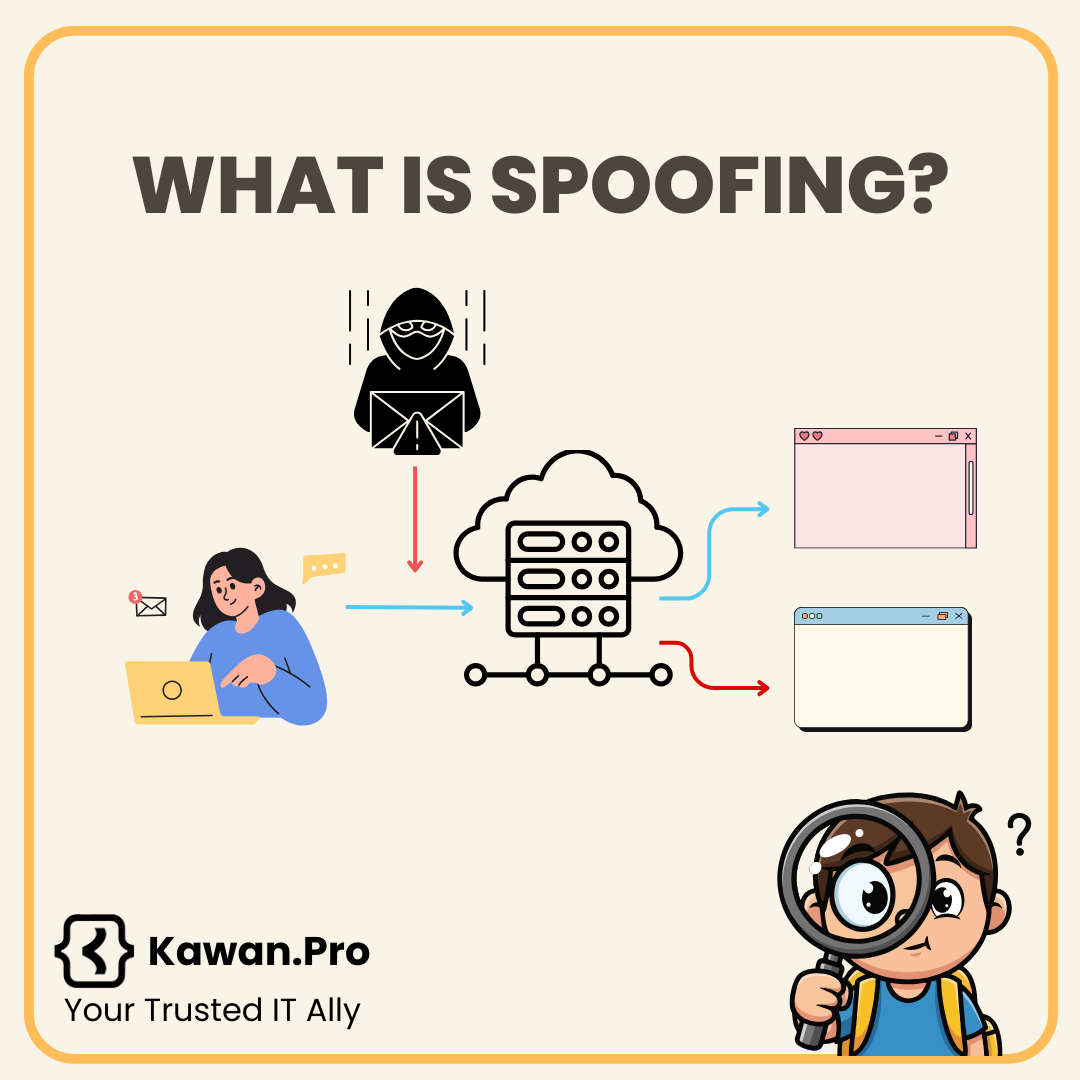
Spoofing is a cyberattack where a malicious actor disguises themselves as a trusted entity to trick systems or users into revealing sensitive information or performing actions.
Instead of being straightforward, the attacker pretends to be someone or something else like a trusted website, email sender, or IP address to bypass security and gain unauthorised access.
Spoofing = fake identity → trick targets into giving access or data
KEY FUNCTIONS OF SPOOFING
(From the attacker’s perspective)
Identity Deception - Pretends to be a legitimate source to gain trust.
Unauthorized Access - By faking credentials or addresses, attackers can enter systems or networks.
Data Theft - Steals sensitive data like login credentials, financial info, or personal details.
Spreading Malware -Tricks users into downloading malicious files or clicking harmful links.
Bypassing Security Measures - Exploits weaknesses in authentication, filtering, or network trust.
WHY IS SPOOFING DANGEROUS?
✔ Sensitive information can be stolen
✔ Accounts or systems can be compromised
✔ Users may unknowingly spread malware
✔ Can be a step in larger attacks (phishing, DDoS, man-in-the-middle)
✔ Often hard to detect without monitoring
Even cautious users and secure systems can be tricked if identity verification is weak.
COMMON TYPES OF SPOOFING
Email Spoofing – Fake sender address in emails
IP Spoofing – Pretending to be a trusted IP address
DNS Spoofing – Redirects users to malicious websites
Caller ID Spoofing – Fakes phone numbers to trick recipients
ARP Spoofing – Intercepts network traffic on local networks
BASIC SPOOFING PREVENTION METHODS
Strong authentication (MFA)
Anti-spoofing protocols (SPF, DKIM, DMARC for email)
Network monitoring & intrusion detection
Keep software and systems updated
Educate users on recognizing suspicious communications
FOUND THIS HELPFUL?
👍 Like if you learned something new
🔁 Share to help others understand cybersecurity basics
🔔 Follow for more simple cybersecurity explainers