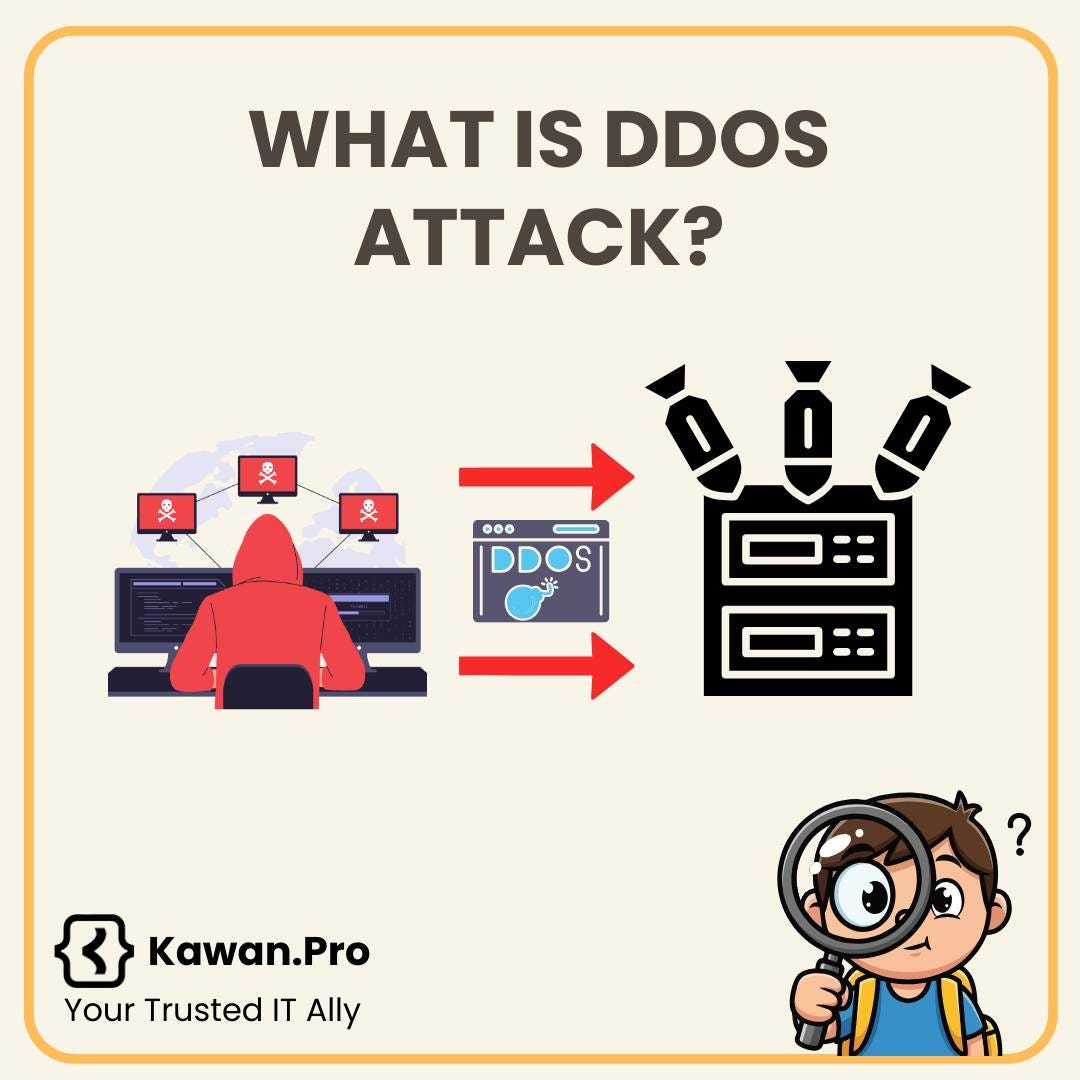
WHAT IS A DDoS ATTACK?
A DDoS Attack (Distributed Denial of Service) is a cyberattack where multiple systems flood a target server, website, or network with massive traffic.
Instead of one computer attacking, thousands or millions of compromised devices (called a botnet) send requests at the same time.This overwhelms the target, causing it to slow down or completely crash.
DDoS Attack = massive fake traffic → service becomes unavailable
KEY FUNCTIONS OF A DDoS ATTACK
(From the attacker’s perspective)
1) Service Disruption
Overloads servers so legitimate users cannot access the service.
2) Resource Exhaustion
Consumes bandwidth, CPU, memory, or connection limits.
3) Availability Impact
Breaks the Availability pillar of the CIA Triad.
4) Financial Damage
Causes revenue loss for online businesses and services.
5) Distraction for Other Attacks
Used to hide data breaches or malware infections.
WHY ARE DDoS ATTACKS DANGEROUS?
✔️ Websites and applications go offline
✔️ Customers lose trust
✔️ Business operations are disrupted
✔️ Can affect critical services (banking, healthcare, government)
✔️ Difficult to trace the attacker
Even well-secured systems can be taken down if availability is not protected.
COMMON TYPES OF DDoS ATTACKS
Volume-Based Attacks – Flood bandwidth (UDP Flood, ICMP Flood)
Protocol Attacks – Exhaust server resources (SYN Flood)
Application-Layer Attacks – Target web apps (HTTP Flood)
Botnet-Based Attacks – Use infected devices worldwide
Amplification Attacks – DNS, NTP, or Memcached abuse
BASIC DDoS PREVENTION METHODS
Firewalls & Rate Limiting
DDoS Protection Services (Cloud-based)
Traffic Monitoring & Alerts
Load Balancers
Redundant Infrastructure
FOUND THIS HELPFUL?
👍 Like if you learned something new
🔁 Share to help others understand cybersecurity basics
🔔 Follow for more simple cybersecurity explainers